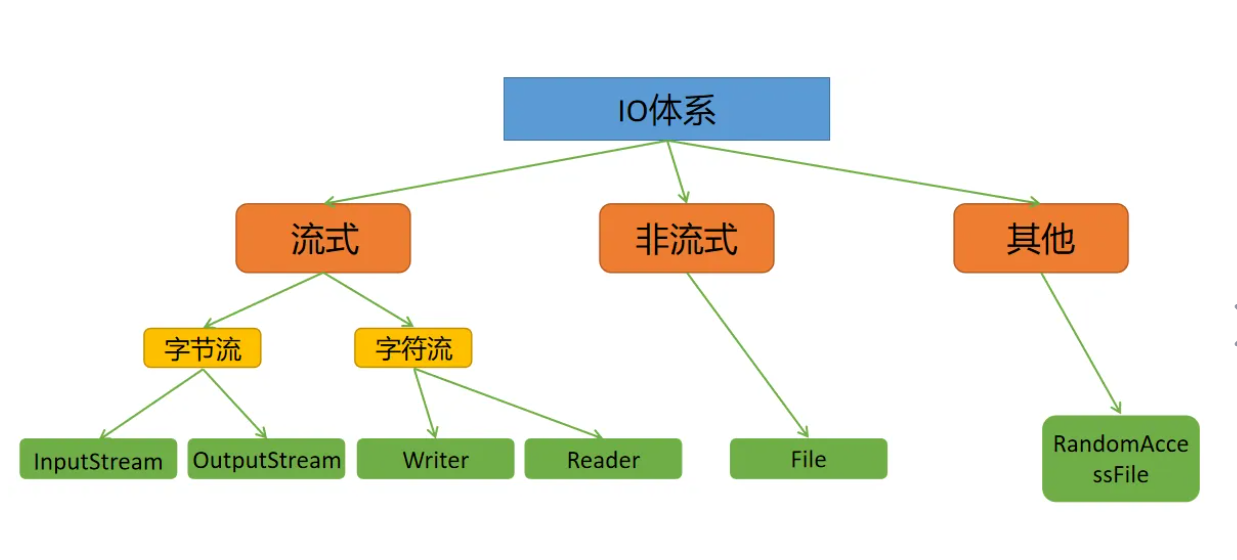
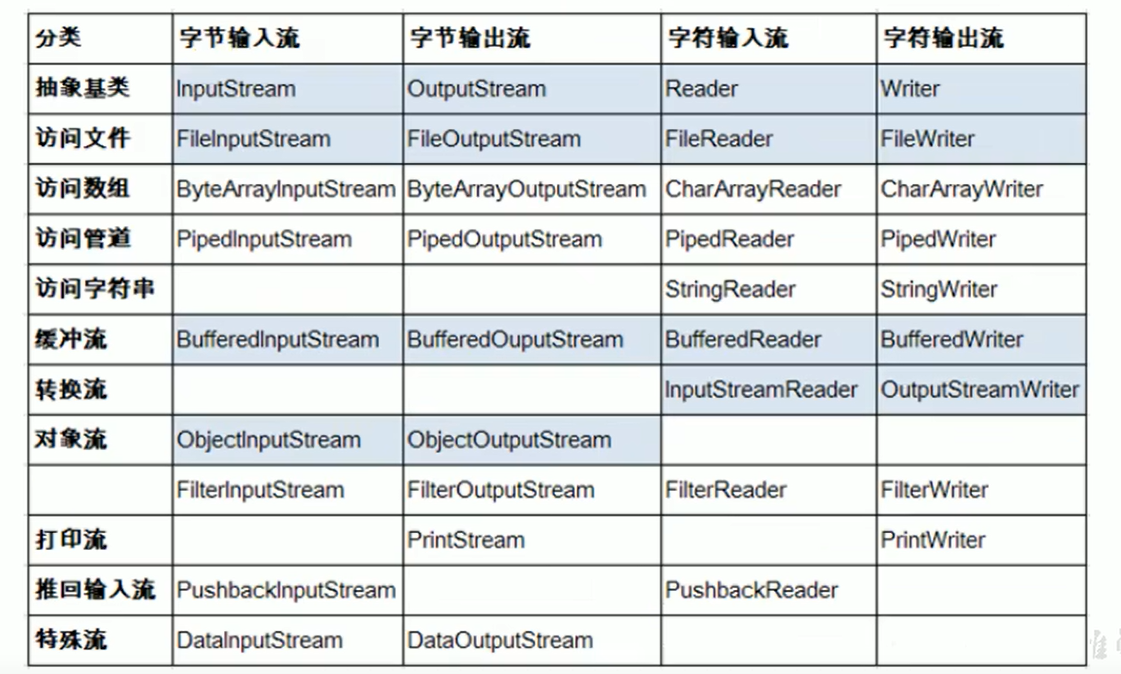
1.IO流概述
IO流是用来处理设备之间的数据传输
对数组的操作是流方式
对于流的操作的类都在IO包中
按流分为输出类 输入流
按角色分为节点流 处理流
按数据类型分为字节流 字符流
流的异常需使用try catch finally处理
1.1流的体系图
2.字符流
字符流主要用于处理纯文本文件
FileReader和FileWriter设计最常用的类
2.1FileReader 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 File file = new File ("a.txt" );new FileReader (file);int data = fr.read();while (data!=-1 ){char )data);
2.2FileWriter 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 File file = new File ("a.txt" );FileWriter fw = new FileWriter (file,true );"zh:这是一个txt类型的文件\n" );"en:this is a file end with .txt\n" );
3.字节流
字节流主要用于处理非文本文件
当只读取数据的时候字节流也可以处理文本文
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 FileInputStream lyo = new FileInputStream ("a.txt" );byte [] bt = new byte [5 ];int len;while ((len=lyo.read(bt)) != -1 ){String s = new String (bt, 0 , len);
3.2FileOutputStream 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @IOAnnotation("字节流适用于除文本文件外文件的复制操作") public static void unTestCopy (String beginPath,String endPath) throws IOException{FileInputStream pic = new FileInputStream (beginPath);FileOutputStream cop = new FileOutputStream (endPath);byte [] bt = new byte [1024 ];int len;while ((len = pic.read(bt)) != -1 ){0 ,len);
4.处理流
处理流就是在原本流的基础上增加功能
处理流也是装配设计模式在Java语言中的体现
4.1缓冲流
缓冲流的内部提供了一个缓冲区域
可以使得数据的读写传输速度更快
在流的体系图中带有Buffered的即为缓冲流
字节流
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Test public void io_Copy () throws IOException {FileInputStream origin = new FileInputStream ("E:\\Videos\\滑板.mp4" );FileOutputStream after = new FileOutputStream ("board.mp4" );BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream (origin);BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream (after);byte [] bt = new byte [1024 ];int len;while ((len = bis.read(bt)) != -1 ){0 ,len);
字符流
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Test public void rw_Copy () throws IOException {BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader (new FileReader ("hello.txt" ));BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter (new FileWriter ("my.txt" ));while ((num = br.readLine()) != null ){"\n" );
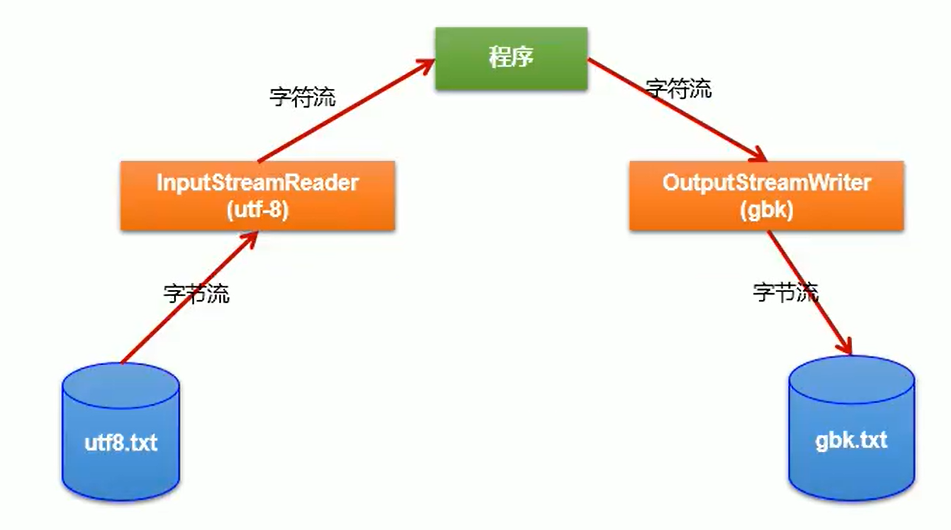
4.2转换流
实现字节流与字符流之间的转换
InputStreamReader 字节->字符 相当于解码的过程
OutputStreamWriter 字符->字节 相当于编码的过程
解码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 FileInputStream files = new FileInputStream ("hello.txt" );InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader (files,"gbk" );int len;char [] cr = new char [10 ];while ((len = isr.read(cr)) != -1 ){String data = new String (cr, 0 , len);
编码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 FileInputStream origin = new FileInputStream ("my.txt" );FileOutputStream after = new FileOutputStream ("my_utf8.txt" );InputStreamReader gbk = new InputStreamReader (origin, "gbk" );OutputStreamWriter utf = new OutputStreamWriter (after, "utf-8" );int len;char [] cr = new char [10 ];while ((len = gbk.read(cr)) != -1 ){0 ,len);
4.3对象流
用于存储和读取基本数据类型或对象
可以把Java对象写入数据源中||从数据源恢复
对象流不能操纵被static和transient修饰的成员变量
反序列化ObjectInputStream
序列化ObjectOutputStream
自定义类序列化
实现serializable接口
提供serialVersionId常量
类中的所有属性也必须是序列化的
对文件的操纵
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 @Test public void OOS () throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("myText.dat" ));new String ("this is a secret file" ));new ObjData (1 ,"banana" ,12.3 ));@Test public void OIS () throws Exception{ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream ("myText.dat" ));Object obj = ois.readObject();String str = (String)obj;ObjData oda = (ObjData)ois.readObject();
4.4其他流 标准输入输出流
System.in 标准输入流
System.out 标准输出流
打印流
PrintStream PrintWriter
java最基本的输出语句就使用到了打印流
数据流
DataInputStream DataOutPutStream
用于读取写出基本数据类型的变量或字符串
4.5 RAF
RandomAccessFile声明在IO中但直接继承Object
即可作为输出流也可作为输入流
实现了DataInput DataOutput接口
创建以后需指定mode参数[r rw rwd rws]说明查看API
作为输入流时会对原本文件内容进行从头覆盖
若使用了seek( )则在指定光标位置插入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 File fl = new File ("1.jpg" );File nfl = new File ("2.jpg" );RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile (fl,"r" );RandomAccessFile rag = new RandomAccessFile (nfl,"rw" );byte [] bytes = new byte [1024 ];int len;while ((len = raf.read(bytes)) != -1 ){0 ,len);
5.File类
在java中对文件和文件目录路径的抽象表示形式
File在这里应该理解为路径,文件路径或文件夹路径
File类提供了对文件操作的基本方法,但没提供修改相关操作,需读写就需要使用IO流
File类对象会作为参数传入IO流中
相对路径:指相较于某个路径下所指明的路径
绝对路径:指包含盘符的所有路径
5.1常用方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 createNewFile 创建指定类型文件File a = new File ("Go.txt" );File b = new File ("Java.txt" );getAbsolutePath () ; 获取绝对路径getPath () ; 获取路径getName () ; 获取名称long length () ; 获取长度字节数long lastModified () ; 获取最后一次修改时间,毫秒值
5.2构造器 根据一个路径得到File对象
根据一个目录和一个子文件/目录得到File对象
根据一个父file对象和一个子文件/目录得到File对象